Categorical encoding:Label-Encoding and One-Hot-Encoder
在机器学习或大数据中,数据集可能包含文本或类别值(categorical values), 基本上是非数值值 (non-numerical values), 例如:颜色:red, orange, blue, white 等、饮食:breakfast, lunch, snacks, dinner, tea。一些算法,比如 CATBOAST,decision-trees 可以很好地处理类别值(categorical values),但大多数算法更偏向使用数值,它们在数值输入时更容易获得 state-of-the-art results。因此我们需要将文本/类别数据转换为数值数据,并仍然使算法/模型从其中习得含义。
有许多将分类值转换为数值的方法,每种方法都有其优缺点。本文主要介绍两种主流的编码方案: One-Hot-Encoding and Label-Encoding. 这两种编码都可用 pandas 或 SciKit-learn 实现。
Label Encoding
将每个类别转化为一个数字 对如下类别值进行 Label Encoding 编码如下:
1 | BRIDGE-TYPE |
Label Encoding: 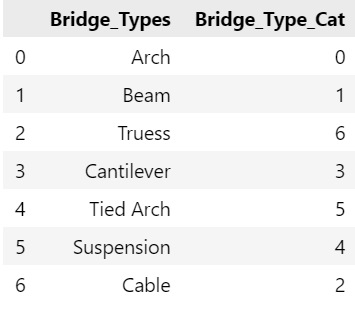
问题与局限
由于 Label Encoding 使用数字序列编码,导致其在原始数据之间引入了关联/比较。很明显在桥的类型没有任何关系。但是从编码角度看,可能会认为 Truess 比 Arch 优先级/次序高。该算法可能会误解数据具有某种层次结构/次序:0 <1 <2…<6,并且可能对 Truess 给予多于六倍的 Arch 的权重
而有些类别,诸如:Safety Level 这类具备优先级/次序的类别值,就可以使用 Label encoding,来标识出其关系。如果算法将 Safety Level 编码解释为: 0 < 1 < 2 < 3 < 4,即 none < low < medium < high < very high, 便是有意义的。
none < low < medium < high < very high
Label Encoding in Python
1 | # import required libraries |
代码提示:
- 默认情况下,非数值型列是 "object" 类型,该方法要求类别列是 "category" 类型,pandas 通过 astype 方法进行类型转换。
- pandas.Series.cat 是 Accessor object for categorical properties of the Series values,返回一个 Categoricals 类型。Categoricals 类型有 categories 和 codes 属性,分别表示数据存储时的分类和编码,用法: pandas.Categorical.categories 与 pandas.Categorical.code。
Using sci-kit learn library approach
1 | import pandas as pd |
结果: 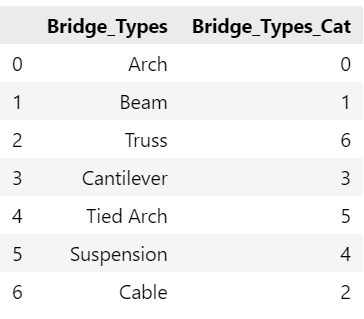
One-Hot encoding
Encoding is a required pre-processing step when working with categorical data for machine learning algorithms. How to use ordinal encoding for categorical variables that have a natural rank ordering. How to use one-hot encoding for categorical variables that do not have a natural rank ordering.